Déjà vu describes the strange experience of a situation feeling much more familiar than it should. Young people experience déjà vu the most. Many of us report our first experiences between the ages of 6 and 10. In this article, we review recent research on déjà vu including what it is, how common it is, and why scientists think it happens.
Déjà vu, pronounced day-zhaa voo, is French for “already seen.” It describes the fascinating and strange experience where you feel that something is very familiar but you also know that this feeling of familiarity should not be as strong as it is. For example, you might be walking to school when you suddenly feel like you have been in exactly this situation before. Of course, you have been in the situation before – you have walked to school many times – but the feeling is so strong and so connected to right now, that you know it should not feel as overwhelming as it does (see Figure 1 for more explanation of what déjà vu is). Déjà vu experiences are often described in movies and books, because they can make people feel like they have somehow seen into the future. They are unusual but cool experiences that can actually tell us a lot about how our minds, particularly our memories, work.
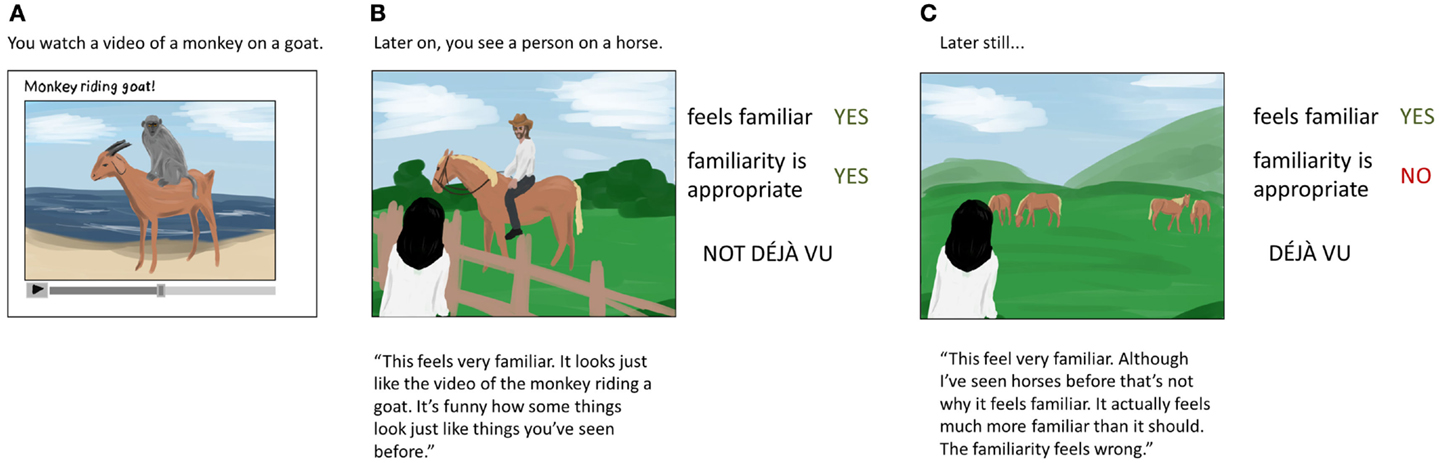
- Figure 1 - What is and what is not a déjà vu experience?
- A. We all go through our lives seeing and experiencing things that we may remember later on. Our memories typically work very well and we can usually trust the feelings of memory we experience. In this picture, you are watching a video of a monkey riding a goat for the first time so it feels like a funny, new thing. B. Sometimes we see and experience things that we recognize or that look like other things we have already seen. When this happens and our memories are working well, we may feel a sense of familiarity. This feeling is entirely appropriate and is not déjà vu. In this picture, you can see a man riding a horse who looks a bit like the monkey riding the goat that you just watched online. Although it is a coincidence that you have seen two such similar things, the feeling of familiarity is appropriate so the sensation you feel is not déjà vu. C. When something feels too familiar, whether it is a thing you recognize or not, and the familiarity feels wrong, you are probably having a déjà vu experience. You often notice this kind of over familiarity because the feeling happens very quickly and then also quickly fades to a normal level of familiarity. In this picture, you see horses and they suddenly feel too familiar. You know that although you have seen horses before they should not make you feel as strongly familiar with them as these horses do. Then, the feeling fades away and you wonder what just happened. That is a déjà vu experience!
In this review, you will read about how often we experience déjà vu. You will then read about how researchers have investigated déjà vu and what they think might cause it.
How Common is Déjà vu?
The percentage of people who experience déjà vu is probably somewhere between 30% (about 8 in a class of 30) and 100% (everyone in a class of 30) [1]. We are not sure about the exact percentage for two important reasons. First, we cannot ask everyone in the world so we have to use the results of surveys of small groups of people. This is a problem because surveys can give us quite different results depending on who we ask. Second, people can give very different answers depending on the definition we give of déjà vu. Asking the question in different ways can get very different results.
We can also get an idea of how often déjà vu happens by asking people. Again, the answers they give depend on who they are and how we ask them the question, but most people report déjà vu somewhere between every few weeks and every few months. Typically, this means that déjà vu is not very common so if you have experienced it recently you are very lucky!
Who Experiences Déjà vu the Most and What Does This Tell Us?
Young people experience déjà vu the most. Having said this, depending on how old you are, you may still have to wait a while until you have your first déjà vu experience. A very small number of people say they had their first déjà vu experience by the age of 6. More people report their first déjà vu experiences as having happened sometime before they were 10 years old. The reason it may take a while to have your first déjà vu experience is that you need to be able to work out whether the feeling of familiarity you have really is stronger than it should be. For many younger kids, this may be a tricky thing to do.
By the time you reach an age between 15 and 25, you will probably be having déjà vu experiences more often than you will ever have them after that. The number of déjà vu experiences people report steadily decreases after 25 years old. This is puzzling for researchers because we are used to thinking of memory problems increasing with age, not decreasing with age! This may actually tell us something really important about déjà vu – that déjà vu is not a memory problem at all. If you think about the stage of déjà vu where you realize that your feeling of recognition should not be as strong as it is, you will probably recognize this is actually a really helpful response. It lets you know that while you may feel really strongly that something is familiar, this feeling is wrong and you should try to ignore it.
Déjà vu may actually be one sign of a healthy mind that is able to spot familiarity signals that are incorrect. Perhaps what is happening in people over the age of 25 is that they get worse at spotting incorrect familiarity signals and they actually start believing them. This is not the only explanation for the change in the number of déjà vu experiences we report as we get older than 25 years though. Can you think of any others?
How Do Scientists Investigate Déjà vu?
Research on déjà vu falls into two main categories: observational studies and experimental studies. In observational studies, researchers measure features of the déjà vu experience (who has it, how often it happens, when it happens, etc.) and look for patterns and links in the results. Observational studies told us that young people have more déjà vu experiences than older people.
In experimental studies, researchers try to trigger déjà vu experiences in people (one of the weirdest ways that this has been done is by squirting warm water into peoples’ ears!). The idea behind many experimental studies is that if we can find out what causes déjà vu, we might be able to understand more about the thought processes that give rise to it.
Experimental studies of déjà vu sound cool, but they are actually really hard to do. We know from lots of experiments that have been done in the past 10 years that it is actually quite easy to get people to say they have had déjà vu in an experiment [2]. We often cannot be sure though, whether people really did have déjà vu or whether they are just saying so. The problem is that people who are doing experiments usually want to give the experimenter the “right” answer.
As an example, if your teacher asked the whole class whether they had ever had déjà vu, and you thought that everyone would put their hands up to say they had, you might do this too, even if you were not sure. There is not anything wrong with this – it is a very normal way to answer questions. The issue is that it does make it hard for researchers to know whether people who say they have had déjà vu have actually had déjà vu, or whether they are just trying to make the researcher happy.
What Causes Déjà vu?
This is a really important question, but it is also still a mystery. We can get some clues from groups of people who report more déjà vu than most. One of these groups contains people who have a condition called “temporal lobe epilepsy.” Epilepsy causes brain cells to send out-of-control electrical signals that affect all the brain cells around them, and sometimes even all the cells in the whole brain. These signals can move through cells in the brain like dominoes, each one knocking over the ones that it is next to. This is called a “seizure” and can result in people with epilepsy briefly losing control of their thoughts or their movements. In people with temporal lobe epilepsy, we know that seizures start in the temporal lobe. This is a part of the brain just inside from the top of your ears, and it is important for making and remembering memories (look at Figure 2 to see where the temporal lobe is).
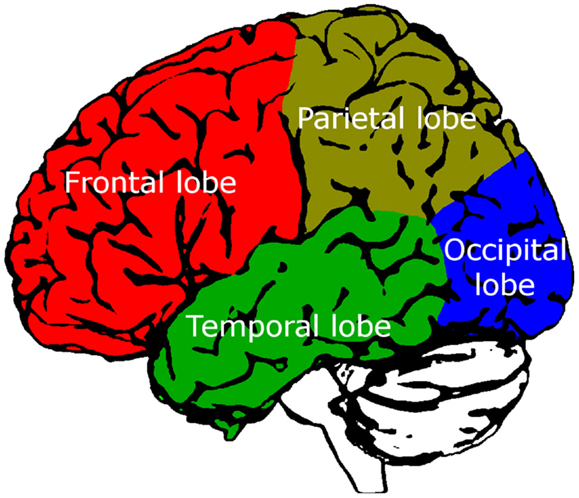
- Figure 2 - The lobes of the brain.
- This colored brain diagram illustrates the lobes on the left hand side of the brain. Two of the lobes we think may play an important role in déjà vu are shown: the temporal lobe (green) and the frontal lobe (red).
Importantly for déjà vu researchers, people with temporal lobe epilepsy often report having déjà vu just before they have a seizure [3]. This tells us that déjà vu is probably linked to the temporal lobe of the brain. In people who do not have epilepsy, déjà vu could be a mini-seizure in the temporal lobe, but one that does not cause any other problems because it stops before it goes too far. This links back to the idea that déjà vu might be caused by a strong feeling of familiarity. The familiarity is signaled by brain cells in the temporal lobe, but is noticed and ignored by another part of the brain that checks whether all the signals coming to it make sense. The part of the brain that does this checking may well be in the frontal lobe, a part of the brain in from just above your eyes. We know the frontal lobe is important for making decisions.
Summary
Déjà vu is an interesting and unusual experience where something feels very familiar, but we know it should not feel as familiar as it does. The experience is important because it shows us that remembering happens with a series of steps, some of which can go wrong. Young people have déjà vu the most, and this may actually be a sign that young people are very good at spotting when their brains start telling them that things are more familiar than they ought to feel. It is very hard to do experiments to make people have déjà vu and we still do not know what actually causes it, but this makes it a very interesting topic for scientists to investigate. Perhaps in the future, you will become a scientist who uncovers the secrets of déjà vu.
Acknowledgements
Our thanks go to Cassie Teale, who created all the artwork used in Figure 1.
References
[1] ↑ Brown, A. S. 2004. The Déjà Vu Experience. New York: Psychology Press.
[2] ↑ O’Connor, A. R., Barnier, A. J., and Cox, R. E. 2008. Déjà vu in the laboratory: a behavioral and experiential comparison of posthypnotic amnesia and posthypnotic familiarity. Int. J. Clin. Exp. Hypn. 56:425–50. doi: 10.1080/00207140802255450
[3] ↑ Bancaud, J., Brunet-Bourgin, F., Chauvel, P., and Halgren, E. 1994. Anatomical origin of déjà vu and vivid ‘memories’ in human temporal lobe epilepsy. Brain 117:71–90. doi: 10.1093/brain/117.1.71
