Abstract
We have all experienced a wound, a local injury to the skin, at some point in our lives. Most often, wounds heal completely and a scab is the only sign of the injury. Except for the initial pain and bleeding, we might not pay much attention to the process by which the wound repairs or the possible complications that could arise. The process of wound healing involves a well-coordinated series of steps involving many cells, tissues, and chemicals in the body. Interruptions to the wound healing process, often caused by the presence of bacteria, lead to major disturbances and delays in wound repair. Further, some forms of bacteria can be resistant to antibiotics, making it difficult to treat infected wounds. In this article, we discuss the stages of wound healing, explain how bacteria can delay this process, and describe simple steps that you can adopt to prevent wound infections.
Introduction
Ouch! Do you remember the last time you fell on the playground and injured your skin? Or accidently slashed your fingertip while using a knife? Maybe it was not very long ago. You might also remember what happened after that. The injury might have oozed some blood, which stopped soon after to reveal reddish, damaged skin. If the injury was deep, you may have visited the doctor. The doctor would have cleaned the damaged skin and covered it with a bandage. Over the next few days, you may have observed the injured skin change colors from bright red to bluish-black, and finally, the injury would have been replaced with fresh skin. After the damaged skin has healed, you may see a flesh-colored scar at the location of the injury. If this sounds familiar, it means that your accidental injury resulted in what is called a wound, which was followed by the normal steps of recovery known as wound healing. It is likely that your wound eventually healed without any problems.
Wounds
The skin is the largest organ of the body and it acts as a protective covering shielding the body from the outer environment. The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, consisting of cells known as keratinocytes. The middle layer, or dermis, contains another type of skin cell known as fibroblasts, and blood vessels that carry blood to and from the skin. The dermis also has tissue fibers that provide support to cells within the skin.
A break in these layers of the skin, often resulting from a blow or cut, can cause a disturbance in the skin’s structure and function, and is known as a wound. Superficial wounds are injuries to only the epidermis. Deep wounds extend all the way into the dermis, causing greater damage to skin cells and tissue fibers, resulting in a gap in the skin. In deep wounds, the blood vessels also get damaged, leading to leaks, which is why these wounds bleed. So, what happens after we get hurt and how does the body respond to a wound?
Wound Healing
After an injury, the body starts repairing damaged skin through the process of wound healing, which involves a set of four well-coordinated steps (Figure 1) [1]. The first step involves stopping the blood flow by formation of a blood clot at the wound, and this happens almost immediately after an injury. To form a clot, blood components interact to form a loose plug of protein strands and blood cells at the wound site. Next, large numbers of immune cells arrive at the wound site through blood vessels, releasing chemicals that start to build new tissue in the wound. In the third stage, the wound is gradually filled with new skin tissue that replaces the gap created by the injury. This works somewhat like building blocks, in which different types of skin proteins act as a solid, sticky surface on which many layers of skin cells can attach and grow. In the final stage of wound healing, this new skin tissue gets strengthened and completely fills the wound. This step replaces the damaged tissue with scar tissue that closely resembles normal skin. This completes the process of wound healing. The entire process of wound healing starts immediately after injury and usually takes a few weeks. However, in certain situations, wounds do not follow this coordinated repair process, taking a long time to heal or not healing at all. Why do some wounds fail to heal properly?
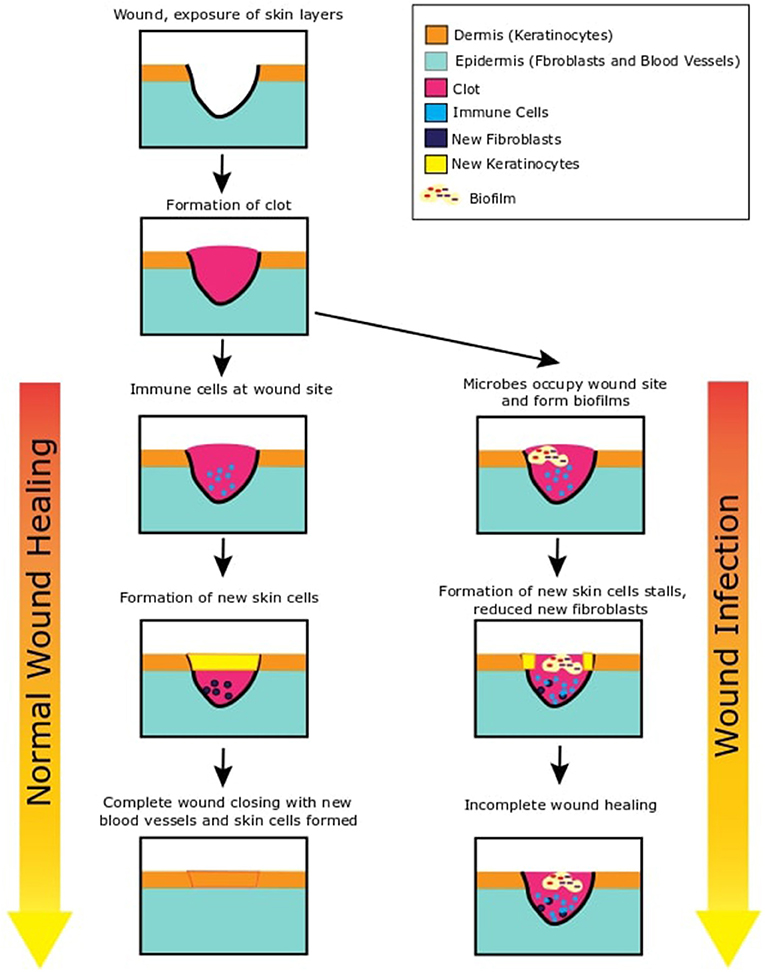
- Figure 1 - This figure shows two possible outcomes after the skin is wounded.
- On the left side of this figure, we see what happens when wounds heal normally. After the skin is wounded, inner layers of the skin are exposed. A blood clot is immediately formed to stop loss of blood. Immune cells migrate to the wound site and release chemicals. These chemical signal the skin layers (epidermis and dermis) to grow new skin cells that move to fill in the gap of the wound. At the end, the newly formed skin tissue strengthens and closes the wound to restore the skin integrity. On the right side of this figure, we can see what is likely to happen in the case of an infection. Bacteria occupy the open wound and start growing and increasing in number. They form biofilms in the wound. They also secrete chemicals to inhibit any protective systems of our skin. As the immune cells cannot clear the bacteria, the infection continues and new skin cell formation is paused. This can remain stalled and result in incomplete wound healing.
Wound Infections
One of the main reasons that wounds may fail to heal properly is the presence and growth of microbes, which are very tiny forms of life, in the wound. Microbes are tiny organisms that cannot be seen with the naked eye. While many microbes are beneficial to us, certain harmful microbes can make us sick, and this is known as an infection. When harmful microbes live and reproduce in a wound, it leads to a wound infection [2]. Wound infections slow down and sometimes prevent the process of healing. Bacteria are the microbes that most often cause wound infections, and a wound can commonly be infected with more than one type of bacteria. But how do bacteria enter wounds in the first place? One possibility is through an object or material that has bacteria on it, like maybe an unclean knife or soil from the playground. Another possibility is that bacteria from the surrounding air can settle on an open wound surface. In fact, this is why doctors often cover wounds with bandages—to prevent exposure to microorganisms in the air. The skin does have defense strategies to remove bacteria that settle on the wound, and often bacteria are killed and wound healing resumes. However, conditions, such as improper cleaning of the wound, poor general health, old age, or diseases, such as diabetes can weaken the skin’s protective systems, increasing the chances of wound infections. These situations may lead to non-healing wounds, which can increase pain, discomfort, and time and money spent in the hospital or on treatment. In extreme cases, spread of the infection can also require the doctors to cut off the infected limb!
A Closer Look at Bacteria in Wounds
Once bacteria enter or settle on damaged skin, the wound provides the necessary nutrients for them to increase in number and spread the infection. In these ideal conditions, individual bacteria grow to form large-scale bacterial communities known as biofilms (Figure 1) [3]. Biofilms consist of large numbers of bacteria clustered together to form dense, mat-like structures that cover the entire surface of the wound [4]. Biofilm bacteria are held together by a mesh of protein and sugars, resembling a glue, often made by the bacteria themselves. This mesh not only strengthens the biofilm structure from within but also serves as a protective covering for the bacteria, surrounding the entire biofilm. When bacteria grow within the wound, they produce small chemicals that are used as signals to communicate with other bacteria as well as to affect immune cells and blood vessels of the host they infect. Immune cells can respond to these signals in an attempt to kill the bacteria and limit spread of the infection. However, the high density of bacteria and the toxic chemicals the bacteria produce can reduce the ability of immune cells to kill the bacteria, making the body unable to remove the biofilm. This results in further growth and spread of the biofilm, which in turn further complicates and delays wound healing.
The removal of wound biofilms requires medical intervention, usually in the form of treatment with antibiotics. Antibiotics are applied as ointments, bandages or by flowing a solution across the wound. Wound biofilms often require multiple applications of antibiotics, over several days. Even if the proper treatment is given, wound biofilms can persist and result in a wound that fails to heal [4].
Why is It Hard to Treat Wound Biofilms?
Biofilm bacterial communities can sometimes survive treatment with antibiotics. One of the reasons for this is the density of bacteria in the biofilm, reminding us of the quote, “united we stand, divided we fall.” Concentrations of antibiotics that work against small numbers of bacteria may not be enough to kill or prevent the growth of large numbers of biofilm bacteria. These bacteria are also embedded in a mesh of proteins and sugars that forms a covering around the biofilm. This mesh can act as a guard, slowing down the entry of antibiotics into the inner parts of the biofilm and protecting the bacteria at the center of the biofilm. Bacteria in biofilms also produce chemicals that can break down certain antibiotics. Finally, biofilm bacteria also have the ability to slow down their growth and reduce their nutrient consumption but still remain alive in a dormant state, with low activity. This tricks the antibiotics, because some antibiotics target only growing bacterial cells. These dormant bacteria can survive antibiotic treatment and begin to grow again when the treatment stops.
What Can Be Done to Help Wounds Heal?
Given the difficulty of successfully treating wound biofilm bacteria with antibiotics, medical doctors and scientific researchers are actively looking for new approaches to eliminate wound biofilms. New methods include applying plant-based extracts to kill microbes, using good bacteria (probiotics) to compete with harmful wound bacteria, exposing the wound to blue light or vacuum forces, or using a combination of these treatments [5]. In any case, the best strategy would be to prevent wound infections, especially among people who are at risk for non-healing wounds. For this, as a young citizen-scientist, the first steps you can take are removing any foreign material from the wound, applying antibiotic ointment, and loosely wrapping the wound in a protective bandage, after which a doctor can evaluate the injury (Figure 2). So, the next time you witness a fall on the playground, you have all the information you need to help yourself and those around you understand wounds, how they heal, what happens when they get infected, and why we should attempt to prevent infections. Ah-ha to that!
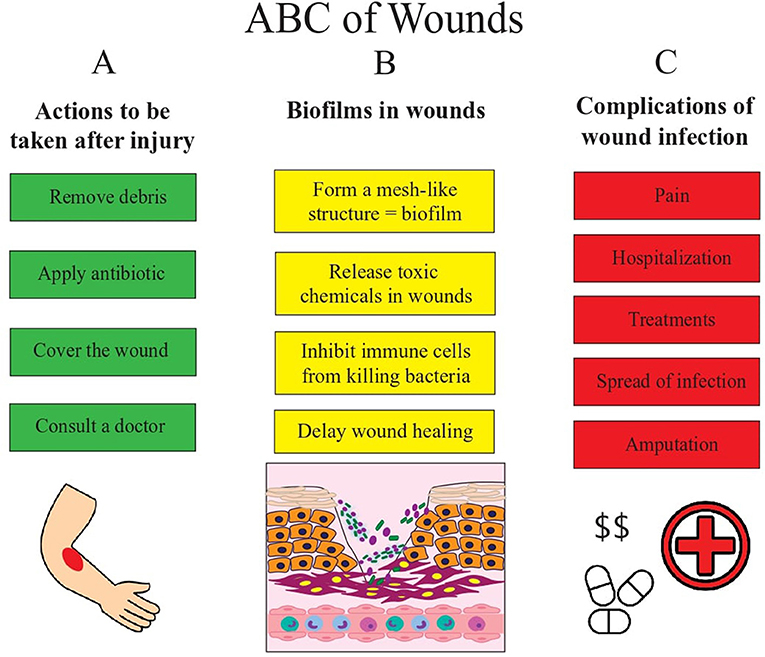
- Figure 2 - This figures shows us the basic ABCs of wounds.
- (A) After the skin is wounded, proper care and treatment is necessary to prevent infection and promote normal wound healing. Wounds need to be cleaned and antibiotics should be applied to prevent infection. In cases of severe wounds or when in doubt on how to proceed, pay a visit to the doctor. If not treated properly, wounds can get infected. (B) Bacteria can enter wounds and form biofilms. They release chemicals that prevent immune cells from killing these bacteria and this delays wound healing. When the number of bacteria in the wound increase even more and the infection becomes severe, it can lead to complications. (C) The non-healing wound can cause a lot of pain and require you to stay at the hospital to get treatment. Infections can also spread to other parts of the body. In some serious cases where even treatment is not helping remove the infection, the doctors may have to cut off the limb or part of the skin where the infection occurs.
Glossary
Epidermis: ↑ The outer layer of your skin. When you look at your skin, you see the topmost part of the epidermis, consisting of dead cells. At the bottom of the epidermis, new cells are made and they gradually move upwards to the surface and continuously replace older cells.
Dermis: ↑ The layer of the skin below the epidermis consisting of blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, oil glands, nerve endings.
Immune Cells: ↑ Cells that defend the body against invaders, such as microbes.
Microbes: ↑ Microscopic forms of life, such as bacteria, viruses, fungi, and protozoa, some of which can cause infections in humans.
Infection: ↑ When harmful microbes enter the body, in a location where they do not belong, it is called an infection. These microbes are harmful to the body in infections.
Biofilm: ↑ A community of bacteria living together within a meshed covering of proteins they secrete.
Antibiotic: ↑ A medicine that kills or prevents the growth of microbes.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
[1] ↑ Gurtner, G. C., Werner, S., Barrandon, Y., and Longaker, M. T. 2008. Wound repair and regeneration. Nature 453:314–21. doi: 10.1038/nature07039
[2] ↑ Bowler, P. G., Duerden, B. I., and Armstrong, D. G. 2001. Wound microbiology and associated approaches to wound management. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 14:244–69. doi: 10.1128/CMR.14.2.244-269.2001
[3] ↑ Costerton, J. W., Lewandowski, Z., Caldwell, D. E., Korber, D. R., and Lappin-Scott, H. M. 1995. Microbial biofilms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 49:711–45.
[4] ↑ Zhao, G., Usui, M. L., Lippman, S. I., James, G. A., Stewart, P. S., Fleckman, P., et al. 2013. Biofilms and inflammation in chronic wounds. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle) 2:389–99. doi: 10.1089/wound.2012.0381
[5] ↑ Kadam, S., Shai, S., Shahane A., and Kaushik, K. S. 2019. Recent advances in non-conventional antimicrobial approaches for chronic wound biofilms: have we found the ‘Chink in the Armor’? Biomedicines 7:35. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines7020035